|
|
|
The Cabinet can be considered the administrative
state body that serves as North Korea’s ‘government’.
However, North Korea’s Cabinet differs in nature
from the traditional concept of the administrative
body as laid down by the principle of checks and
balances.
Functionally, the Cabinet is an ‘administrative
executive body’ or a ‘state management body’ while
politically it is an inferior body, subject to direction
and supervision by the KWP (Korea Workers’ Party)
and the SPA (Supreme People’s Assembly). As of 2005,
the Cabinet consists of 33 divisions including two
committees, 27 ministries, a research institute,
a bank, and two bureaus (‘guks’). The Cabinet is
headed by the Premier, with several Vice Premiers
and Ministers (‘Sangs’), who are in charge of each
ministry. These positions are appointed by the SPA
every 5 years. |
|
|
|
 Functions of the Cabinet
Functions of the Cabinet |
 Drawing
up measures to implement state policies Drawing
up measures to implement state policies
 Enacting/amending
regulations concerning state management, in accordance
with the Constitution and other relevant laws Enacting/amending
regulations concerning state management, in accordance
with the Constitution and other relevant laws
 Supervision
of the Cabinet’s committees, ministries, attached
divisions, and regional people’s committees Supervision
of the Cabinet’s committees, ministries, attached
divisions, and regional people’s committees
 Creating
or disbanding organizations directly subordinate
to the Cabinet, key administrative and economic
organizations, and factories Drawing up measures
to improve national management organizations Creating
or disbanding organizations directly subordinate
to the Cabinet, key administrative and economic
organizations, and factories Drawing up measures
to improve national management organizations
 Drawing
up and implementing national economic development
plans Drawing
up and implementing national economic development
plans
 Drawing
up and implementing the national budget Drawing
up and implementing the national budget
 Organizing
and executing projects in industry, agriculture,
construction, postal service, trade, territorial
management, urban management, education, science,
culture, health, athletics, labor administration,
environmental conservation, tourism, etc. Organizing
and executing projects in industry, agriculture,
construction, postal service, trade, territorial
management, urban management, education, science,
culture, health, athletics, labor administration,
environmental conservation, tourism, etc.
 Drawing
up measures to enhance the monetary and financial
system Drawing
up measures to enhance the monetary and financial
system
 Exercising
control and inspection to maintain social order Exercising
control and inspection to maintain social order
 Drawing
up measures for maintaining social order, as well
as protecting the rights of the people and the interests
of state and social cooperative organizations Drawing
up measures for maintaining social order, as well
as protecting the rights of the people and the interests
of state and social cooperative organizations
 Conducting
foreign policy, such as ratifying treaties Conducting
foreign policy, such as ratifying treaties
 Canceling
decisions or measures by administrative and economic
organizations that run contrary to those of the
Cabinet Canceling
decisions or measures by administrative and economic
organizations that run contrary to those of the
Cabinet
The Premier, representing
the government, organizes and directs Cabinet-run
projects. |
|
 Duty and Operation of the Cabinet
Duty and Operation of the Cabinet |
Task - Execution and supervision of national administration
Duty - Must answer to the SPA (or the Standing Committee
if the Assembly is in recess) on domestic affairs
Full Meeting - attended by all Cabinet members.
Cadre Meeting - attended by the Premier, Vice Premiers,
and other Cabinet members to discuss matters delegated
from the full meeting |
|
 Regional People’s Committee
Regional People’s Committee |
Regional People’s Committees serve as regional
governments on provincial, city, and county levels.
Chairmen, Vice Chairmen, Secretaries, and members
are elected every four years.
Main Functions :
△organizing and executing all administrative affairs
within the pertaining region,
△implementing laws and measures legislated by the
pertaining Regional People’s Committee, superior
Committees, the SPA, and the Cabinet,
△drawing up and implementing measures for economic
development in the pertaining region,
△ drawing up and implementing regional budgets,
△supervising projects executed by subordinate committees |
|
 Administrative System of North Korea
Administrative System of North Korea |
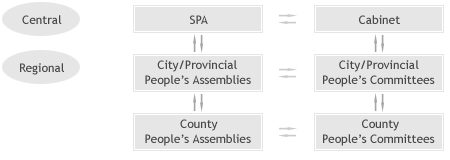
(↓= supervises, → = appoints & supervises, ↑
←= answers to) |
|
|
 |
|